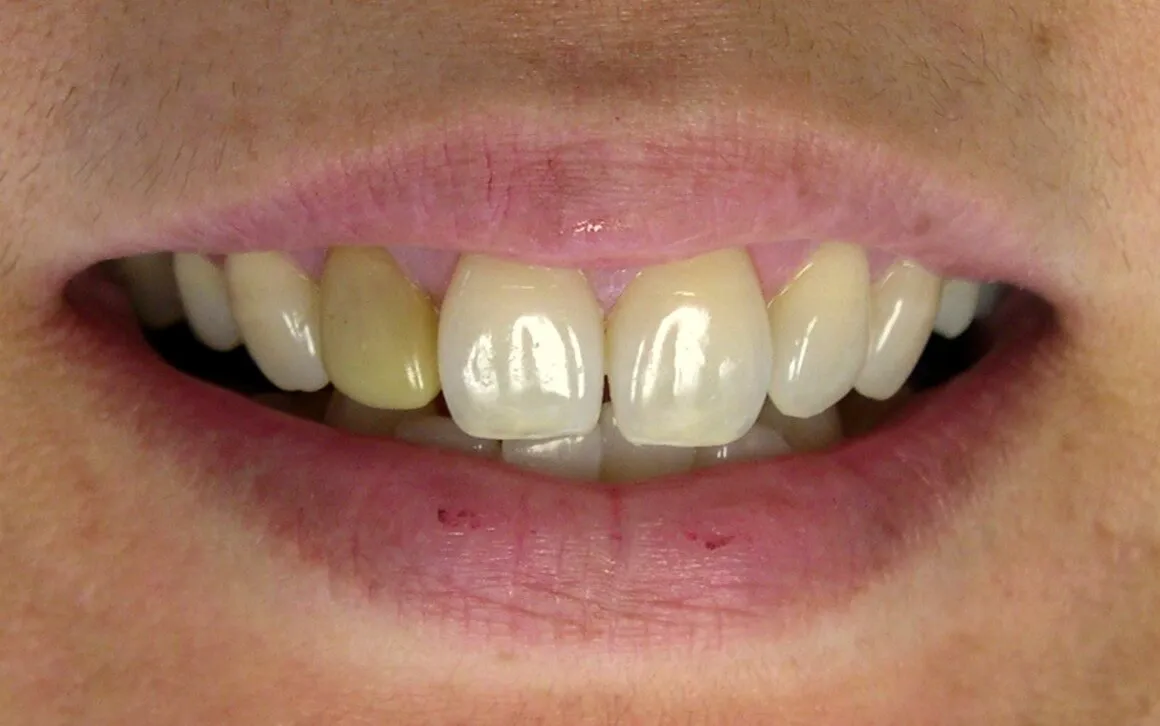
Understanding Teeth Whitening Bleach and Gum Contact
Teeth whitening has become a popular cosmetic procedure, promising brighter smiles. However, the chemicals used in these treatments, particularly bleach, can pose risks if they come into contact with your gums. Understanding these risks is crucial for anyone considering teeth whitening, whether at home or in a professional setting. This article dives into the potential dangers of teeth whitening bleach and how to mitigate them, ensuring both a dazzling smile and healthy gums. The interaction of teeth whitening agents and gum tissues can lead to various adverse effects, ranging from minor irritation to severe complications. This comprehensive guide explores the top five risks associated with teeth whitening bleach on gums, helping you make informed decisions about your oral health. This includes understanding the type of bleach used, its concentration, and how it interacts with the sensitive tissues of the gums. The goal is to empower you with the knowledge to protect your gums and ensure a safe teeth whitening experience.
The Chemistry of Teeth Whitening and Gum Sensitivity
Teeth whitening products typically use bleaching agents like hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These chemicals work by penetrating the enamel and breaking down the stain-causing molecules. However, the same properties that make them effective on teeth can also be detrimental to your gums. The sensitivity of gums to these chemicals is a key factor in the risks associated with teeth whitening. Gums are composed of soft tissues that are highly vascularized, meaning they have a rich blood supply. This makes them more susceptible to irritation and absorption of chemicals. The concentration of the bleaching agent plays a significant role in the potential for gum damage. Higher concentrations, often used in professional treatments, pose a greater risk if not handled carefully. The pH level of the whitening agent also affects its interaction with the gums. Acids can further irritate the delicate gum tissue, increasing the risk of chemical burns and sensitivity. Understanding this chemistry is fundamental to grasping the potential hazards.
Risk 1 Chemical Burns and Irritation from Bleach
One of the most immediate risks of teeth whitening bleach on gums is chemical burns. This occurs when the bleaching agent comes into direct contact with the gum tissue, causing irritation and inflammation. The severity of the burn can vary depending on the concentration of the bleach and the duration of exposure. Mild burns may manifest as redness and slight tenderness, while more severe cases can result in significant pain, blistering, and even tissue damage. The initial symptoms of chemical burns often include a stinging or burning sensation, followed by the whitening of the affected area. This is due to the bleaching action on the superficial layers of the gums. If the exposure continues, the gums may become inflamed, swollen, and painful to the touch. This can interfere with eating, drinking, and even speaking. The overall health of the gums is also impacted.
Symptoms of Chemical Burns
Recognizing the symptoms of chemical burns is crucial for prompt treatment. The most common symptoms include a burning sensation in the gums, a white or blanched appearance of the affected areas, redness, swelling, and tenderness. Blisters or ulcers may also develop in severe cases. These symptoms can appear within minutes to hours of exposure to the bleaching agent. The intensity of the symptoms often correlates with the concentration of the bleach and the duration of contact. If you experience any of these symptoms after teeth whitening, it’s important to rinse your mouth with water and seek advice from a dentist immediately. Avoid brushing the affected area aggressively and refrain from using any further whitening treatments until the gums have healed. Quick action can prevent further complications and ensure faster recovery, minimizing the risk of long-term damage to your gums.
How to Identify Irritation
Distinguishing between mild irritation and a more serious chemical burn involves careful observation. Mild irritation may present as slight redness and sensitivity. While mild irritation might resolve on its own, it’s crucial to take preventative measures. Examine your gums regularly for any changes in color or texture. If you notice any unusual whiteness, swelling, or blisters, it’s important to seek professional advice. The location of the irritation can provide clues about the source. For example, if the irritation is concentrated along the gum line, it likely indicates that the bleach has come into direct contact with your gums. In addition to visual examination, pay attention to any discomfort you experience, such as pain, tingling, or a burning sensation. Understanding these early signs will help you take proactive steps to protect your gums.
Risk 2 Gum Recession and Sensitivity

Gum recession, a condition where the gum tissue pulls back, exposing more of the tooth and its root, is another potential risk associated with teeth whitening. While not always directly caused by the bleach itself, the irritation and inflammation from chemical exposure can weaken the gum tissue and make it more susceptible to recession. Repeated exposure to bleaching agents can exacerbate this process. This recession can lead to increased tooth sensitivity, as the roots lack the protective enamel of the crown. This sensitivity can be triggered by hot, cold, sweet, or sour foods and drinks. Gum recession can also increase the risk of cavities and gum disease. The exposed roots are more vulnerable to decay, and the receding gums provide a less effective barrier against bacteria and plaque. Maintaining good oral hygiene, regular dental checkups, and using protective measures during teeth whitening can help prevent gum recession and mitigate its effects. Regular dental visits can help monitor your gums and catch any signs of recession early on.
Causes of Gum Recession due to Bleach
While bleach doesn’t directly cause gum recession, it can contribute to it through several mechanisms. Inflammation and irritation caused by the bleach can weaken the gum tissue, making it more prone to damage. This damage can make the gums less able to withstand brushing and other forces, leading to recession over time. Improper application techniques during teeth whitening, such as using trays that don’t fit properly, can also cause the bleach to seep onto the gums. This repeated exposure can lead to chronic inflammation and increase the risk of recession. Individuals with pre-existing gum conditions, such as gingivitis or periodontitis, are at a higher risk of developing recession following teeth whitening treatments. The bleaching agents can irritate their already inflamed gums, further compromising their health. Proper application and monitoring are essential to minimize the risk. The long-term effects of repeated exposure to bleaching agents can further accelerate this process.
Impact on Tooth Sensitivity
Tooth sensitivity is a common side effect of teeth whitening, especially if the bleach comes into contact with the gums. When the gums recede, the roots of the teeth become exposed. These roots lack the protective enamel, making them highly sensitive to external stimuli. Even if the gums do not recede, the chemicals in bleach can penetrate the enamel and dentin, leading to temporary sensitivity. This sensitivity can manifest as sharp, shooting pains or discomfort when consuming hot or cold food and drinks. For some individuals, the sensitivity can persist for several days or even weeks after the whitening treatment. Using desensitizing toothpaste containing potassium nitrate or other active ingredients can help to alleviate this discomfort. Additionally, avoiding acidic foods and drinks during and after the treatment period can also help to reduce sensitivity. If the sensitivity persists or becomes unbearable, it’s important to consult with a dentist to rule out any underlying dental issues and to get advice on how to manage the pain. There is also a risk of developing a painful condition called pulpitis if the bleach reaches the pulp of the tooth.
Risk 3 Allergic Reactions and Oral Health Issues
Allergic reactions, while less common, can occur when the bleach or other components of teeth whitening products come into contact with the gums. These reactions can range from mild to severe, and it’s important to be aware of the signs and symptoms. Beyond allergic reactions, teeth whitening can also contribute to other oral health issues if not performed correctly or if proper precautions are not taken. Understanding these potential problems can help you make informed decisions and seek timely treatment if any issues arise. Furthermore, the overall health of your mouth plays an important role in the success of the whitening process and avoiding complications. It’s important to maintain a good oral hygiene routine.
Identifying Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions to teeth whitening products can manifest in several ways. Symptoms may include swelling of the gums, lips, or tongue, which can lead to difficulty breathing. Other signs include skin rashes, itching, and hives around the mouth. Contact dermatitis, characterized by a red, itchy rash, can also occur where the bleach has come into contact with the skin. The symptoms typically appear shortly after the teeth whitening treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, seek immediate medical attention, as severe allergic reactions can be life-threatening. Before undergoing teeth whitening, inform your dentist about any known allergies. It’s essential to identify the allergen to avoid it in the future. If a mild reaction occurs, antihistamines can help to manage the symptoms, but professional evaluation is always advised to rule out more serious underlying health concerns. The use of hypoallergenic products can also help prevent reactions.
Other Oral Health Complications
Besides allergic reactions, teeth whitening can lead to other oral health complications if not performed correctly. The over-whitening of teeth can cause irreversible enamel damage, making them more susceptible to staining and decay. Excessive use of bleaching agents can also irritate the soft tissues of the mouth, leading to inflammation and discomfort. If teeth whitening is performed on teeth with existing cavities or cracks, the bleach can penetrate these areas, causing increased sensitivity and pain. The chemicals can also interact with existing dental work, such as fillings or crowns, causing them to become discolored or damaged. Bleeding gums during or after the whitening process can also be a sign of inflammation or underlying gum disease. It is very important to consult with a dentist before undergoing any teeth whitening procedure to ensure your mouth is healthy and to discuss any potential risks and complications.
Risk 4 Long Term Damage and Complications
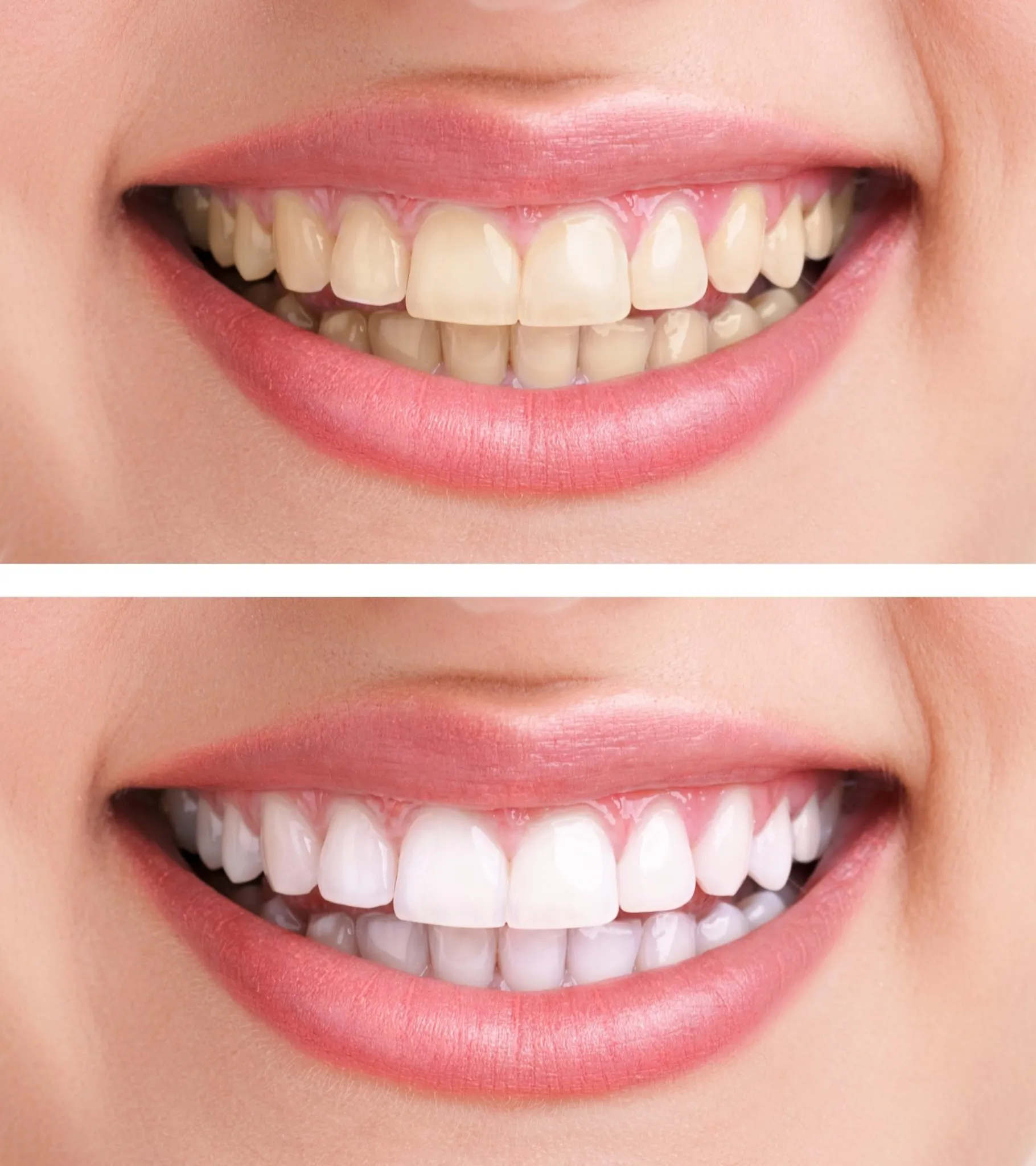
Repeated exposure to teeth whitening bleach can lead to long-term damage and complications, even if immediate symptoms are mild. The cumulative effect of chemical exposure can weaken the enamel over time, making teeth more vulnerable to staining, decay, and sensitivity. The delicate gum tissues, repeatedly exposed to these chemicals, may experience chronic inflammation, which can eventually contribute to gum disease. The extent of the damage depends on the concentration of the bleach, the frequency of treatments, and the individual’s oral health and hygiene practices. Prolonged exposure can also increase the risk of other oral health problems, such as increased tooth sensitivity and damage to the pulp. Proper guidance and safe practices are vital to protect your oral health.
The Effects of Repeated Exposure
Repeated teeth whitening treatments can have significant long-term effects on both the teeth and the gums. Each whitening session exposes the enamel and dentin to bleaching agents, which can cause microscopic changes to the tooth structure. Over time, this can lead to increased porosity of the enamel, making the teeth more susceptible to staining from food, drinks, and tobacco. The repeated exposure to bleaching agents can also affect the bond strength of dental restorations, such as fillings and crowns, potentially leading to premature failure. The gums can also suffer from repeated exposure, as the chemical irritants may cause chronic inflammation, predisposing individuals to gum disease. Proper care between whitening sessions, such as using desensitizing toothpaste, can help reduce some of the negative effects. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are also essential to monitor the health of your teeth and gums and to address any problems promptly. The cumulative effects of repeated exposure can also alter the natural balance of the oral microbiome.
Long Term Oral Health Concerns
The long-term oral health concerns associated with teeth whitening involve more than just the appearance of your teeth. Enamel erosion can increase the risk of cavities and tooth decay, as the protective outer layer of the teeth becomes thinner and more vulnerable to acids. The repeated irritation of gum tissue can contribute to chronic inflammation and gum disease, leading to tooth loss if left untreated. The increased sensitivity caused by enamel erosion can make it difficult to enjoy hot and cold foods and drinks. Furthermore, the chemical effects of bleach can also contribute to changes in the oral microbiome, potentially affecting the overall health of the mouth. To minimize these risks, it is essential to follow your dentist’s instructions carefully, limit the frequency of teeth whitening treatments, and maintain excellent oral hygiene. This includes regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups. Taking a break between whitening treatments also gives your teeth and gums a chance to recover and rebuild their natural defenses. If there is any concern it is always a good idea to consult a dentist.
Risk 5 Incorrect Application and Improper Use
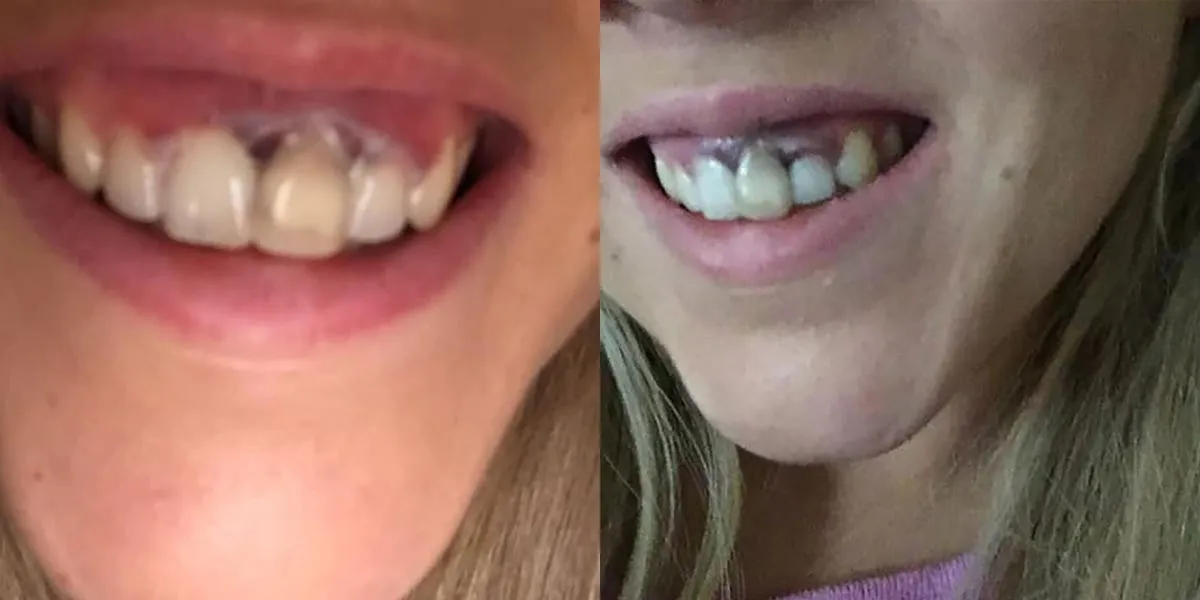
Incorrect application and improper use of teeth whitening products are significant contributors to the risk of gum damage. This is especially true with home-based treatments, where users may not have the professional training and guidance to ensure safe and effective use. Inaccurate application can lead to direct contact of the bleach with the gums, causing irritation and chemical burns. Using too much bleach or leaving it on for longer than recommended can exacerbate these problems. Choosing the wrong type of whitening product for your specific needs and dental condition can also increase the risk of complications. Understanding the proper use of these products, whether at home or in a professional setting, is essential to prevent gum damage and maximize safety. Furthermore, it is important to follow all instructions carefully to avoid unwanted side effects. Always consult your dentist or a qualified dental professional.
Common Application Errors
Common application errors during teeth whitening can lead to various problems, including gum irritation, chemical burns, and increased tooth sensitivity. A common error is using too much bleaching agent in the trays, which can overflow and come into contact with the gums. Another error is not ensuring a proper fit of the whitening trays, which can cause the bleach to leak onto the gums. Leaving the whitening solution on for longer than the recommended time can also cause increased damage to the gums. Failing to protect the gums properly with a barrier before applying the bleach is another common mistake. Some users may also use the wrong concentration of bleach or the wrong type of product for their specific dental condition, increasing the risk of adverse effects. Always read and follow the instructions on the product package. If you are undergoing a professional treatment, make sure your dentist uses proper application techniques.
Importance of Professional Guidance
Professional guidance is crucial for safe and effective teeth whitening. Dentists and other qualified dental professionals have the training and expertise to assess your oral health, determine if teeth whitening is appropriate, and recommend the best treatment option for your specific needs. They can also ensure that the procedure is performed safely and correctly, minimizing the risk of gum damage and other complications. A dentist can provide custom-fitted trays that ensure the bleach is applied evenly and does not come into contact with the gums. They can also monitor your progress and adjust the treatment as needed. Furthermore, they can offer advice on how to manage any side effects, such as tooth sensitivity. Choosing a professional teeth whitening treatment ensures that you are receiving care from someone with the knowledge and experience to provide safe and effective results. Always consult with your dentist before undergoing any teeth whitening procedure.
Preventing Gum Damage During Teeth Whitening
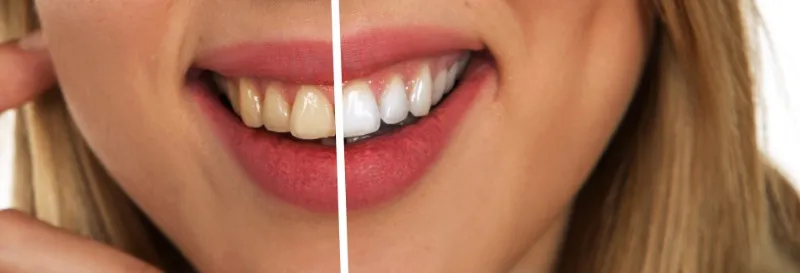
Protecting your gums during teeth whitening is essential to minimize the risks of irritation, damage, and long-term complications. Several measures can be taken to ensure the safety of your gums while still achieving the desired whitening results. This starts with choosing the right products and following the correct application techniques. Protective measures, such as using custom-fitted trays, applying a gum barrier, and rinsing your mouth thoroughly after each treatment, can help protect your gums from exposure to the bleach. Additionally, consulting with a dentist before undergoing teeth whitening is crucial to determine the best approach for your specific needs and oral health condition. Taking these precautions can significantly reduce the potential for gum damage and help you achieve a brighter, healthier smile.
Using Protective Measures
Using protective measures is a crucial step in preventing gum damage during teeth whitening. Custom-fitted trays are one of the most effective protective measures, as they ensure that the whitening agent is applied evenly to the teeth and does not come into contact with the gums. If you are using over-the-counter whitening products, make sure to follow the instructions carefully. Another essential protective measure is using a gum barrier. This can be applied by a dental professional to protect the gums from exposure to the bleaching agent. Rinsing your mouth thoroughly with water after each whitening treatment can help remove any excess bleach that may have come into contact with your gums. This can help to reduce the risk of irritation and chemical burns. Avoiding over-whitening and following your dentist’s recommendations for treatment duration and frequency is also essential. If you experience any discomfort during the whitening process, stop the treatment immediately and consult your dentist.
The Role of a Dentist
The role of a dentist in teeth whitening is paramount, ensuring both the safety and effectiveness of the procedure. Before any whitening treatment, a dentist will conduct a thorough examination of your teeth and gums. They will assess your oral health, identify any existing conditions, and determine if you are a suitable candidate for teeth whitening. Dentists can provide professional-grade whitening treatments, which typically involve higher concentrations of bleaching agents. They can also provide custom-fitted trays. Dentists will provide you with detailed instructions, and also monitor your progress. They will also be able to suggest the best course of treatment. If any complications arise, they will be able to address them promptly, minimizing the risk of long-term damage. Furthermore, they can advise on the best oral hygiene practices to maintain your results. Consulting with a dentist is the safest way to achieve a brighter, healthier smile, minimizing the risks associated with teeth whitening.